The future of EV charging - hubs
What does the current data say and where is the industry headed?
An EV charging hub refers to a site with more than 10 charging points, which can include both CCS2 and Type2 connectors. These hubs are publicly accessible to all EV users, though some charging points may be reserved for captive users like fleet operators. We have excluded these reserved points from our numerical analysis.
In this article, we'll explore the locations of these hubs and examine the strategy behind establishing such large charging facilities. We'll investigate why certain Charge Point Operators (CPOs) are investing in this model, while others remain skeptical. The 2412 release of EVInfraBI contains extensive data, which you can access today. We'll explore some key insights from the tool in this article.
P.S.: This is a premium article for ExpWithEVs. You can subscribe or refer this publication to others to get access to all premium articles.
Before we get to the article, here's some housekeeping:
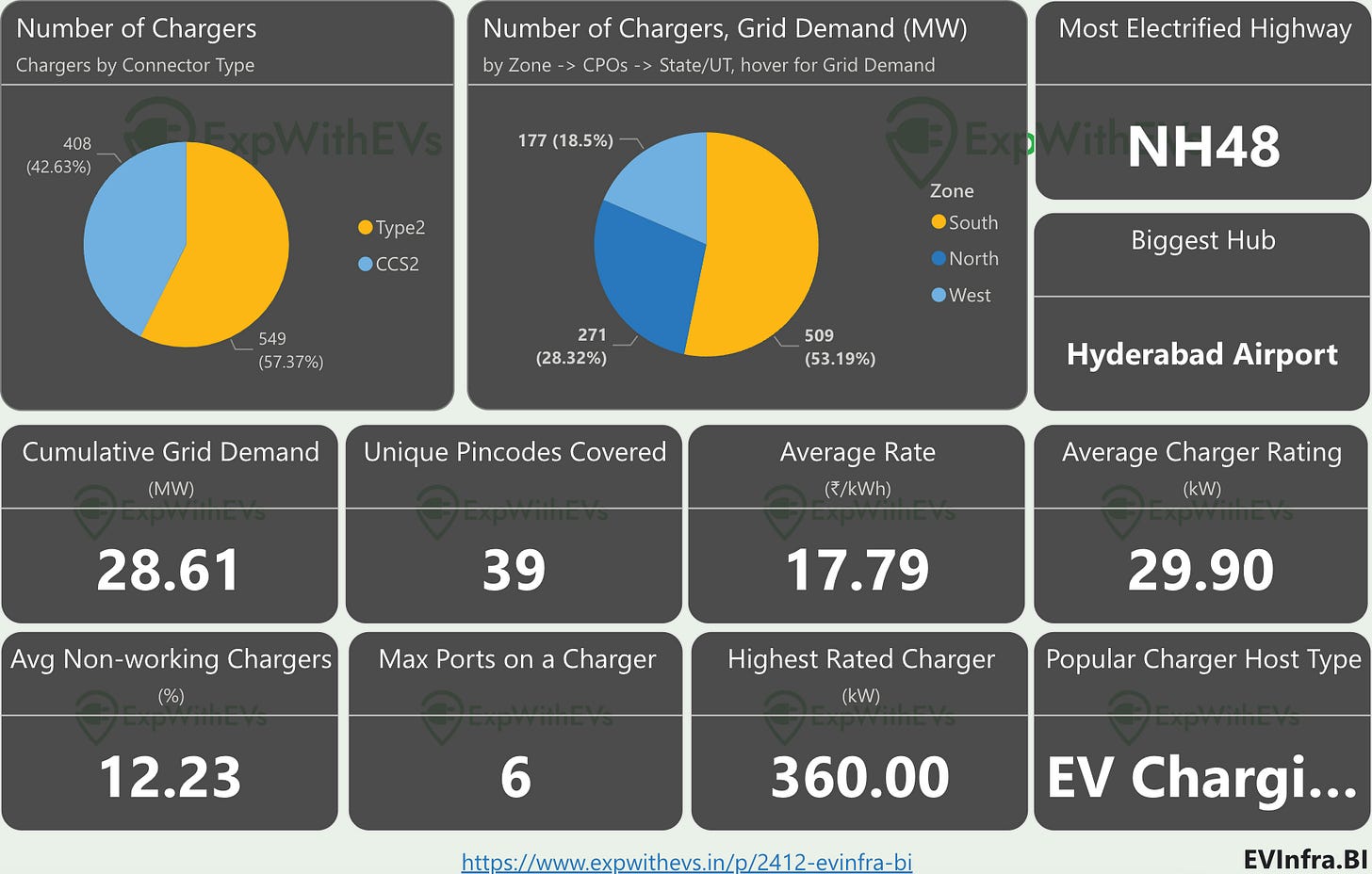
We've just released our 2412 EVInfraBI update, featuring detailed data on charging locations from over 40 CPOs. The tool now shows charger hosting sites, geographic details, rates, power ratings, and more. New features include highway charger analysis, charging hub locations (concentrated charging points at single sites), and "jodi chargers" (different CPOs' chargers within walking distance). Get your team onboarded today!
We've also released 2412 EVTrendsBI, offering a high-level overview of charging infrastructure trends and growth in the Indian EV industry. Get access to it today!
I'll be attending the India Energy Week on 11th February 2025. Drop me a message if you'll be around or fill this form.
Later in February, I'm taking my MG ZS EV to a national park in India. The route covers three modern expressways, though charging infrastructure remains sparse. Ensure you are subscribed to not miss the article!
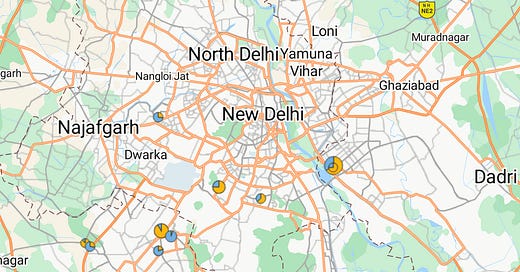
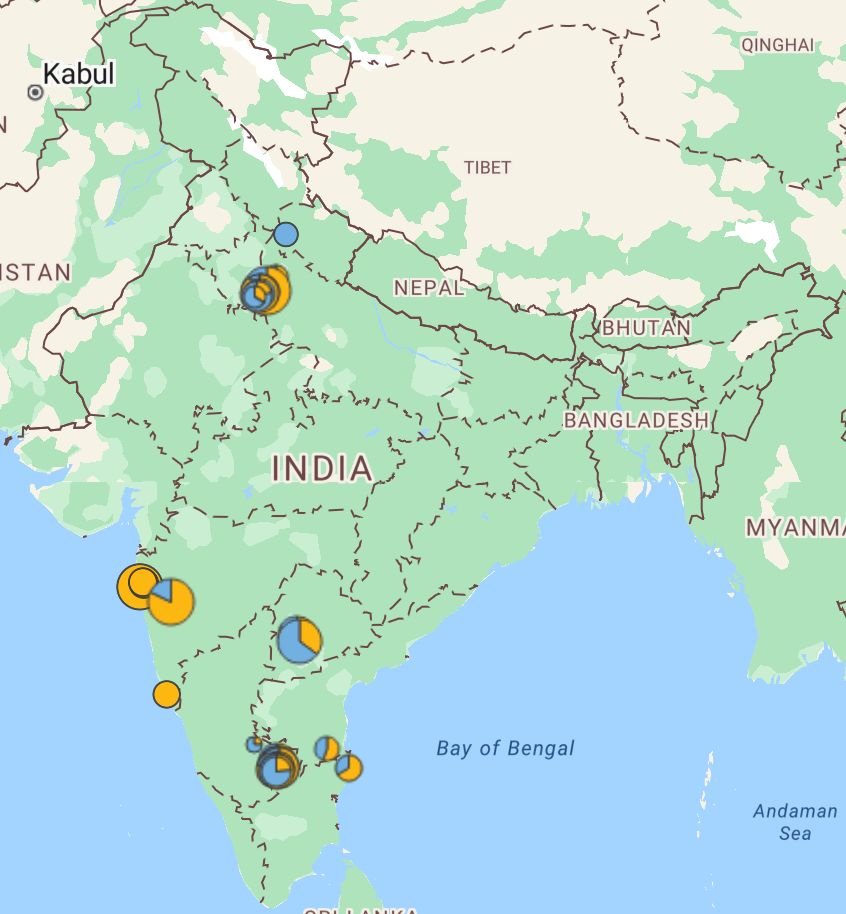
Around 10% of India's CCS2 and Type2 public charging network exists in hubs. These hubs are predominantly located in the North and South zones. They span ten states: Andhra Pradesh (South), Delhi (North), Goa (West), Haryana (North), Karnataka (South), Maharashtra (West), Tamil Nadu (South), Telangana (South), Uttar Pradesh (North), and Uttarakhand (North).
The South Zone accounts for more than 50% of the total grid demand across public charging hubs. The West Zone has significantly fewer hubs relative to its total number of charging points. No public hubs exist in the Central, East, or North East regions of the country.
Jio-bp and Glida own the majority of these charging points. Other operators include
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to ExperiencesWithEVs to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.